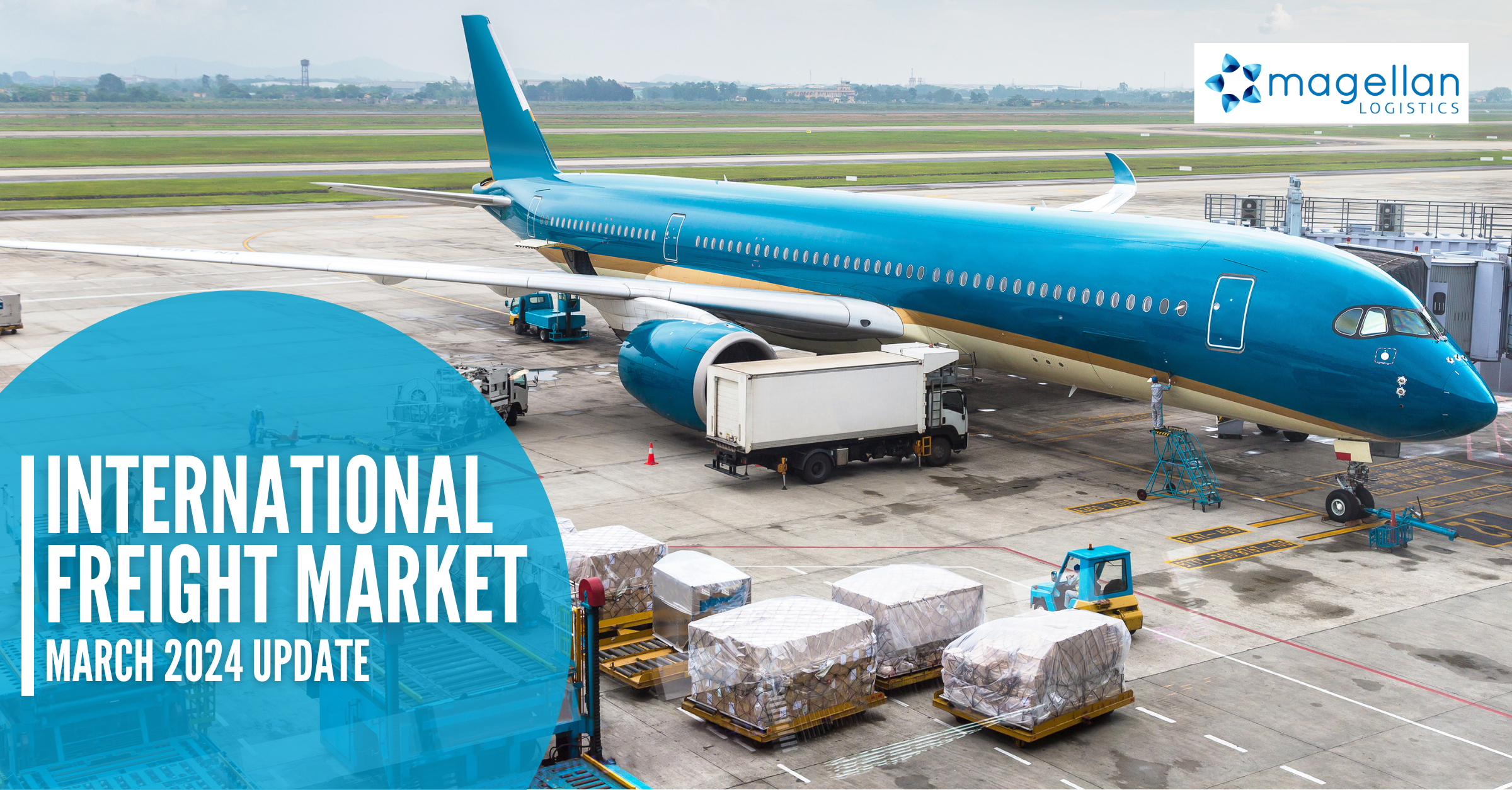
The multifaceted role of a freight forwarder in modern logistics is often misunderstood. However, its pivotal importance in global trade cannot be understated. A forwarder serves as a crucial intermediary between the shipper, consignee and transportation services, taking on the task of organising shipments for corporations or individuals. Their primary objective is to ensure that goods are transported from the producer or manufacturer to a final distribution point efficiently and cost-effectively as possible.
Freight forwarders negotiate the best possible price to move the product along the most economical route. They do this by analysing various bids and selecting the one that optimally balances speed, cost, and reliability. However, the role of a freight forwarder extends far beyond mere price negotiations; they also manage and oversee a multitude of logistical details involved in shipping goods across borders.
The rich history of freight forwarding traces back to the 19th century, coinciding with the advent of rail and road transport. Over the subsequent decades, the industry has expanded and evolved alongside the inception of air and sea transport. With growing complexities in global trade and the necessity for better coordination and handling of multiple modes of transportation, freight forwarding has become more structured and organised. In our modern, globalised world, the freight forwarder is an indispensable provider of logistical solutions for international trade.
Significance and influence of freight forwarding in today’s global economy
Today’s global economy is intricately interconnected, and freight forwarding is the engine that keeps this complex machinery running. Freight forwarders make international trade viable, ensuring goods and products reach their intended destinations promptly and efficiently. As the masterminds orchestrating global logistics, they stimulate economic growth, foster international cooperation, and propel businesses across the globe towards success.
A freight forwarder is much more than a shipping agent; they’re a partner in logistics management, contributing to your business growth by guaranteeing a smooth supply chain operation. This, in turn, leads to enhanced customer satisfaction and increased business profitability.
Decoding the principles: The forwarder’s perspective
The freight forwarding process is initiated when a client provides a consignment. The freight forwarder then utilises their established relationships with transport providers to move the goods from the point of origin to the final destination. The freight forwarder’s responsibilities are vast, including negotiating prices, choosing the optimal mode of transport, and managing the logistical challenges of international trade.
The freight forwarding process involves several key players: the shipper, the carrier, the consignee, and of course, the freight forwarder. Each plays a distinct but vital role, contributing to the smooth movement of goods across borders. As the linchpin in this intricate network, the freight forwarder coordinates between all parties to ensure a seamless transaction and timely delivery.
Exploring the different modes of transportation: air, sea, and land
Freight forwarders have many transportation modes at their disposal – air, sea, and land. The choice of transport mode is a strategic decision made by the freight forwarder based on various factors such as cost, distance, the nature of goods, and delivery timelines. For example, perishable goods like fruits or vegetables are often transported by air due to the speed of delivery, ensuring freshness upon arrival. Conversely, bulky, non-perishable items are commonly shipped by sea or rail, as these methods are more cost-effective for large quantities.
The freight forwarder’s expertise lies in evaluating these factors and making informed decisions that optimise shipping efficiency, thereby saving their clients time and money.
Delving into the core processes involved
Freight forwarding is far more than merely moving goods from point A to point B. It encompasses many processes, each crucial in ensuring a successful transaction. Let’s delve into the core processes involved in freight forwarding.
Shipping documentation and customs clearance
Freight forwarders handle all the crucial paperwork, including the bill of lading, commercial invoices, and insurance documents. They are experts in navigating the labyrinthine customs regulations, ensuring goods comply with all relevant laws in the origin and destination countries. This meticulous attention to detail helps to minimise potential delays or penalties.
Cargo packing, storage, and inventory management
Freight forwarders also oversee goods’ proper packing, storage, and inventory management. The freight forwarder ensures that goods are securely packed, suitably stored in warehouses if necessary, and effectively tracked to ensure stocks are accurately managed. These processes are crucial for preventing damage or loss during transit.
Booking and managing transportation and logistics
On behalf of shippers, freight forwarders book and manage transportation, coordinating with multiple carriers and employing different modes of transport as necessary. Their role involves ensuring timely delivery and handling unexpected contingencies such as delays or disruptions in the supply chain.
Risk management and insurance in freight forwarding
Freight forwarders also help manage risk by advising regarding cargo insurance for potential losses or damages during transit. They can suggest the appropriate level of coverage and handle insurance claims should issues arise.
Understanding the legal and regulatory aspects of freight forwarding
Navigating the World of International Trade Laws and Regulations: A complex web of international trade laws and regulations governs the freight forwarding industry. These laws impact various aspects of freight forwarding, such as customs clearance, handling of hazardous materials, and compliance with international trade agreements.
The essential role of freight forwarders in compliance with trade laws
Freight forwarders play an instrumental role in ensuring compliance with these laws. They stay abreast of changes in regulations, guide clients on compliance issues, and can help mitigate costly fines and penalties.
Grasping the key international agreements and conventions impacting freight forwarding
Various international agreements and conventions, such as the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) terms and conventions under the World Trade Organization (WTO), shape the global freight forwarding landscape. Understanding these agreements and conventions is essential for freight forwarders to ensure compliance with international trade rules.
Embracing technology and innovation
In an era defined by digital transformation, technology is playing an increasingly influential role in reshaping freight forwarding. Innovations such as tracking and tracing systems, digital freight platforms, and automated documentation are significantly increasing efficiency and reducing errors in the freight forwarding process.
This digital transformation in freight forwarding is creating a new level of transparency and enhancing customer service. Clients can now track their shipments in real-time, access documentation online, and communicate more efficiently with freight forwarders. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) will provide innovative solutions in freight forwarding in the coming years. These technologies offer tools for predictive analytics, enhance security and transparency, and improve logistics efficiency.
Addressing the challenges and opportunities in freight forwarding
Despite its crucial importance, the freight forwarding industry faces several challenges, including the rise of trade protectionism, regulatory complexities, and environmental concerns. Additionally, the industry is under pressure to adapt to the rapid digital transformation currently revolutionising logistics.
However, these challenges also present opportunities. Digital transformation, for example, allows freight forwarders to enhance service delivery, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. Moreover, the increasing demand for environmentally friendly logistics solutions opens opportunities for innovative, sustainable practices.
Freight forwarders can prepare for the future by embracing digital technologies, prioritising sustainability, and continuously adapting to regulatory changes. Investing in staff training and development is also crucial to navigating the evolving industry landscape. By doing so, freight forwarders can ensure they remain at the forefront of global trade, facilitating the efficient movement of goods across borders.
The future outlook
The future of forwarding looks promising. With continuous innovation and technological advancements, the industry is set to become more efficient, transparent, and customer-focused. The era of digitalisation is making freight forwarding more streamlined and straightforward, enhancing customer experience and service delivery.
As we move into this future, freight forwarders who adapt, evolve, and innovate will play a crucial role in shaping the global trade landscape, propelling economies, and fostering international cooperation. The world will always need goods to move, and freight forwarders will always be there to ensure they do so in the most efficient, cost-effective, and reliable manner possible.
Magellan Logistics provides freight and logistics services to all industries, including sea freight, air freight, customs clearance and the all-important digital freight portal providing 24/7 visibility of all your shipments. Get in touch with one of our freight specialists on 1300 651 888.