As a result of our economic ties and China’s position as the world’s manufacturing hub, many Australian and New Zealand businesses are looking to import goods from China. The process of importing from China to Australia and New Zealand can be both rewarding and challenging. This article will guide you through the critical aspects of importing goods from China, including product regulations and safety standards, shipping, Goods and Services Tax (GST), and import duties. This comprehensive guide will help you navigate the complexities and ensure a successful import experience.
Identifying a trustworthy supplier in China
Finding a reliable supplier is one of the most critical steps in the importing process. Working with a supplier who can provide quality products, reliable delivery, and clear communication is essential. This can be achieved through researching potential suppliers, obtaining samples, and reviewing their credentials and certifications.
Here are some tips to help you find a reliable supplier in China:
Research potential suppliers
Start by conducting thorough research on potential suppliers. You can find suppliers through online marketplaces, trade shows, and directories.
Obtain samples
Once you have identified potential suppliers, obtaining samples of their products is essential. This will help you determine the quality of their products and ensure that they meet your specific requirements.
Review credentials and certifications
It is critical to review their credentials and certifications before working with a supplier. Ensure they have the necessary licenses and certifications to manufacture and export their products.
Build a relationship
Building a relationship with your supplier is crucial to ensure clear communication and a smooth importing process. Regular contact through email, phone, or video calls can help build trust and ensure that you and your supplier are on the same page.
Product regulations & safety standards
Before you begin importing goods from China, it’s crucial to familiarise yourself with the relevant product regulations and safety standards in Australia. These standards are designed to protect consumers and ensure the quality of imported products. Here are the primary organisations and regulations you should be aware of:
- Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC): The ACCC enforces product safety and compliance with mandatory standards. Consult the ACCC’s guidelines for the specific goods you’re importing.
- Australian Border Force (ABF): This organisation oversees the import process and ensures that imported goods comply with all relevant laws and regulations.
- Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry (DAFF): DAFF enforces biosecurity regulations for imported goods, ensuring that they don’t pose a risk to the environment or human health.
- Australian Electrical Regulatory Authorities Council (ERAC): If you’re importing electrical products, they must meet the relevant safety and performance standards established by ERAC.
- Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority (APVMA): For importing products related to agricultural or veterinary chemicals, you must comply with the APVMA’s standards.
- Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA): If you’re importing medical devices, pharmaceuticals, or other health products, they must meet the TGA’s regulatory requirements.
- CITES Australia: The Department of Climate Change, Energy and the Environment and Water handles the importation of CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species) products which can include leather articles such as handbags or footwear
- Department of Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development and Communications manages the importation of motor vehicles into Australia, which are prohibited without import approval being pre-arranged.
It’s essential to research the specific product regulations and safety standards applicable to your imported goods. Non-compliance can result in fines, seizure of goods, or even legal action.
Product labelling
Product labelling requirements are a crucial consideration when importing from China to Australia. It is essential to adhere to the following labelling guidelines:
- AS/NSZ Labelling Requirements: Specific product standards may include labelling specifications that must be followed.
- Ingredients Labelling: Food, cosmetics and certain products require mandatory ingredient labelling.
- Country of Origin: Food products and imported goods that require a ‘trade description’ must display the country of origin.
- Care Labelling: Apparel and textiles necessitate care labelling instructions.
- RCM Mark: Electronic products should bear the RCM Mark, which has replaced the A-Tick and C-Tick marks.
- The Commerce (Trade Descriptions) Regulation 2016 outlines general labelling requirements on all imported products.
Please note that no universal set of labelling requirements applies to all products. Verifying the specific requirements that apply to your product’s label is essential.
Most suppliers will not be aware of the applicable labelling requirements. Please provide them with pre-prepared label artwork to guarantee compliance.
Shipping from China to Australia
Once you’ve ensured that your products comply with Australian regulations, the next step is to arrange shipping from China to Australia. There are two primary methods of shipping: air freight and sea freight.
Air Freight: This method is ideal for time-sensitive shipments or products with a short shelf life. Air freight is generally more expensive than sea freight but offers the advantage of faster delivery times, usually between 3-5 days.
Sea Freight: For larger shipments or products with a longer shelf life, sea freight is the more economical choice. Sea freight delivery times can range from 18-30 days, depending on the specific route and shipping company.
When selecting a shipping method, consider cost, delivery time, and the nature of your goods. You’ll also need to choose a reputable freight forwarder who will handle the logistics of transporting your goods from China to Australia. Be sure to evaluate the services of multiple forwarders, reliability, and customer reviews to ensure the best fit for your business.
Goods and services tax (GST)
A Goods and Services Tax (GST) of 10% in Australia is levied on most imported goods. The GST is calculated based on the value of the imported goods plus the cost of international transport, insurance, and any import duties. If you’re registered for GST in Australia, you may be able to claim a GST credit for the tax paid on your imported goods.
It’s important to note that there are some exemptions from the GST, including certain food items, medical supplies, and products that qualify for the “low-value import threshold.” The low-value import threshold is currently set at AUD 1,000.
Duties when importing from China
In addition to the Goods and Services Tax (GST), import duties may also apply to your imported goods. Import duties are calculated based on your goods’ Customs Value (CVAL), including the cost, shipping fees, and insurance. The rate of import duties varies depending on the type of goods and their country of origin.
You must classify your goods using the Harmonized System (HS) code to determine the applicable import duty rate. The HS code is a globally standardised system that assigns a unique number to each product type. You can search for the HS code for your products on the Australian Border Force (ABF) website or consult a customs broker for assistance.
China–Australia Free Trade Agreement (ChAFTA)
The China-Australia Free Trade Agreement (ChAFTA), which entered into force in 2015, has significantly reduced or eliminated import duties on many products originating from China. To take advantage of ChAFTA’s preferential tariff rates, you must ensure your goods meet specific rules of origin requirements and provide a Certificate of Origin (COO) from the relevant Chinese authority. Ensure that your supplier understands these requirements and can provide the necessary documentation.
Import processing charge
The Australian government levies an Import Processing Charge (IPC) on imported goods which is collected by the Australian Border Force (ABF). The IPC is based on the mode of transport (air or sea) and the imported goods’ Customs Value (CVAL). The IPC rates are subject to change, so it’s essential to check the current rates on the ABF website or consult a customs broker.
Customs value (CVAL)
The Customs Value (CVAL) is crucial in determining the amount of import duties and GST payable on your imported goods. The CVAL is calculated based on the transaction value of the goods, which includes the price paid or payable for the goods and any additional charges such as origin shipping fees, insurance, and commissions.
In some cases, the transaction value may not accurately reflect the true value of the goods (for example, in cases of related party transactions). In these situations, the Australian Border Force (ABF) may use alternative valuation methods, such as the transaction value of identical or similar goods, the deductive value method, or the computed value method.
Import licenses and permits
Depending on the type of goods you’re importing, you may need to obtain an import license or permit from the relevant Australian government department or agency. Import licenses and permits are designed to regulate the importation of certain goods to protect public health, safety, and the environment.
For example, if you’re importing food products, you may require a permit from the Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry (DAFF). Or, suppose you’re importing chemicals or hazardous substances. In that case, you may need a permit from the Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority (APVMA) or the National Industrial Chemicals Notification and Assessment Scheme (NICNAS).
Ensure that you research the specific import license and permit requirements for your goods before importing them to avoid potential delays or penalties.
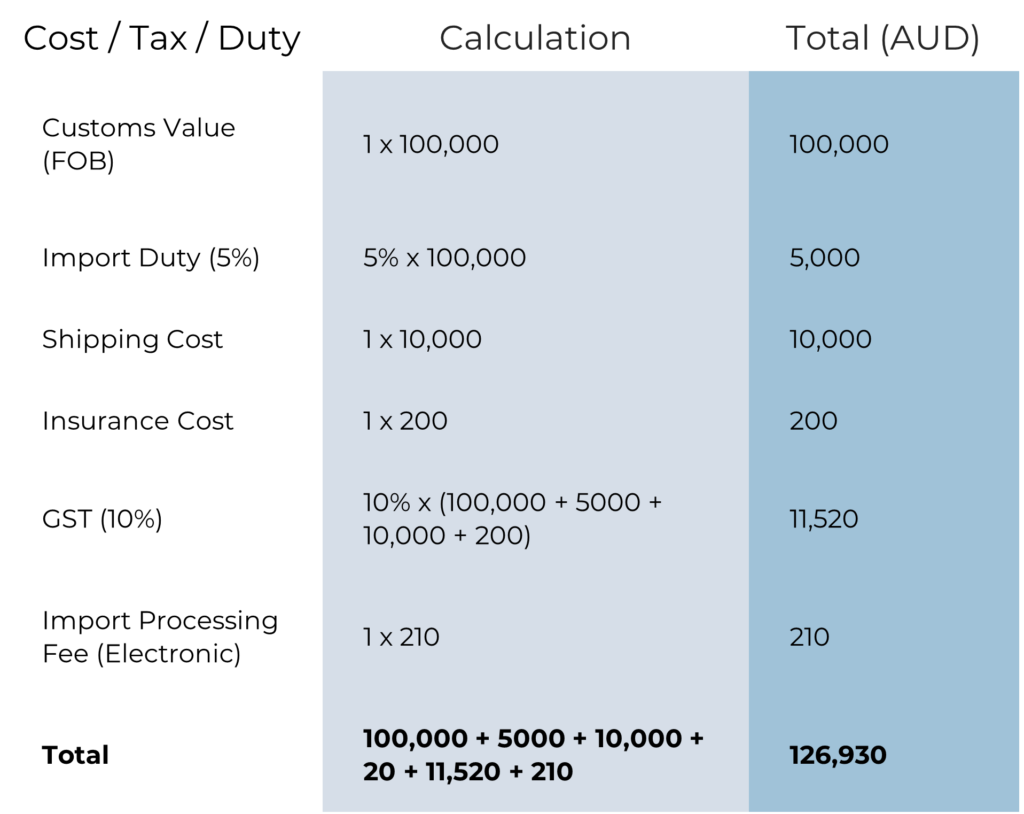
Total import tax cost calculation
To calculate the total import tax cost for your goods, you’ll need to consider the following components:
Import Duties: These are calculated based on the Customs Value (CVAL) and the applicable import duty rate for your goods, as determined by the HS code.
Goods and Services Tax (GST): The GST is levied at a rate of 10% on the value of the imported goods, plus the cost of international transport, insurance, and any import duties.
Import Processing Charge (IPC): This is a government charge based on the mode of transport and the CVAL of the imported goods.
Magellan’s team of customs brokers is specially trained and licensed to handle all customs and quarantine requirements and routinely deal with importers, exporters, port authorities, and governments. We are Australian Trusted Trader accredited, recognising our secure supply chain and compliant trade practices. Our ATT status provides a range of trade facilitation benefits, helping us quickly address the complexities of the border clearance process. With over 25 year’s experience in handling cross-border trade with China, we are your ideal partner for importing your cargo from China to Australia.
In addition to customs brokerage, Magellan provides freight and logistics services to all industries, including sea freight, air freight, and the all-important digital freight portal, providing 24/7 visibility of all your shipments. Get in touch with one of our freight specialists on 1300 651 888.